There are countless business models on the internet and this can be overwhelming to a lot of people. So if you wanted to startup then I’m sure your startup will be one of these 31 business models.
What are the different types of startups? 🔗
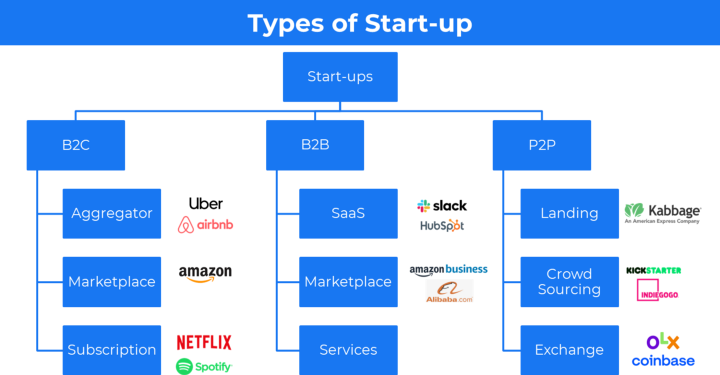
So grab a coffee and let’s dive in…
Freemium Business Model (Freemium = Free + Premium) 🔗
The freemium business model allows users to utilize basic features of a software, game or service for “free”, and then charges for “upgrades” to the basic package.
Examples: Google Drive, iCloud and Slack
The idea here is to provide users with a basic, functional, and free version of your product or service.
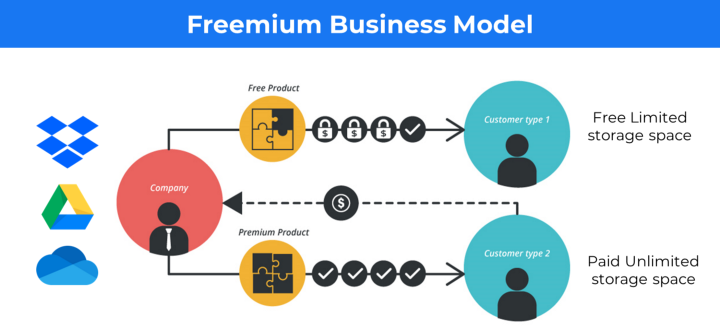
Google Drive and Dropbox, will give you 15GB and 2GB of free space but charge a premium if you buy some additional space.
You can read more about the Freemium business modelhere)
Subscription Business Model 🔗
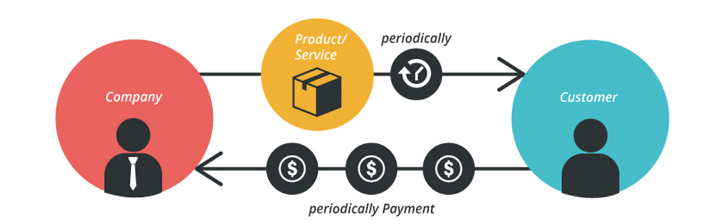
Subscription business models are based on the idea of selling a product or service to receive monthly or yearly recurring subscription revenue.
Examples: Tinder, Netflix, Shopify etc.
It is the next step to the Freemium business model only if a customer is interested in paying monthly for a product to use some premium features.
Marketplace business model 🔗
It is a type of e-commerce site or mobile app where products or services are sold to customers with third-party sellers.
Examples: Amazon, Fiverr etc.
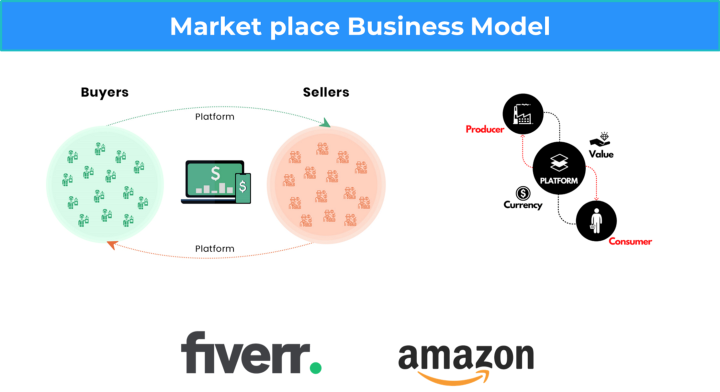
- Amazon has a third-party seller who sells their product on their platform
- Fiverr has freelancers who provide specific services like graphic design.
Aggregator business models 🔗
In the aggregator business model, the service is delivered to customers under their brand name.
Example: Uber, Airbnb etc.
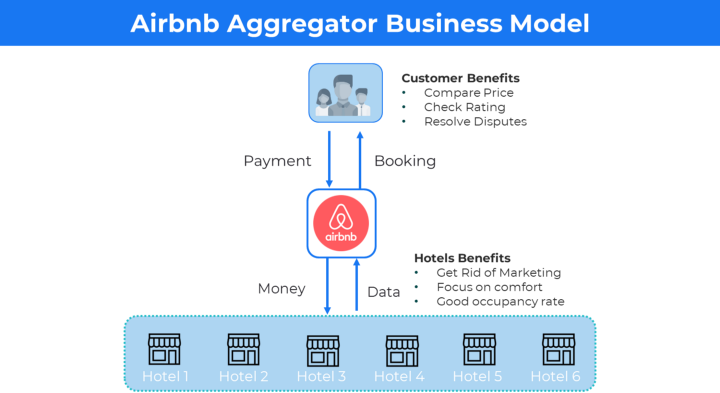
Aggregators have a slight difference between Marketplace and Aggregator business models.

Marketplaces like Amazon and Fiverr connect vendors and customers and take a revenue cut (10%–20%) from these vendors.
An aggregator like Uber and Airbnb onboard these vendors and provide offerings under their brand names.
Pay-as-you-go business model 🔗
This is a pricing strategy where users pay based on how much they consume. It is widely used by cloud computing companies.
Example: Google Cloud Platform(GCP), Amazon Web Service (AWS)
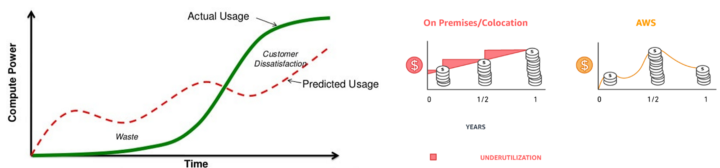
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon that offers over 200 cloud services, each of which has its own pay-as-you-go pricing system.
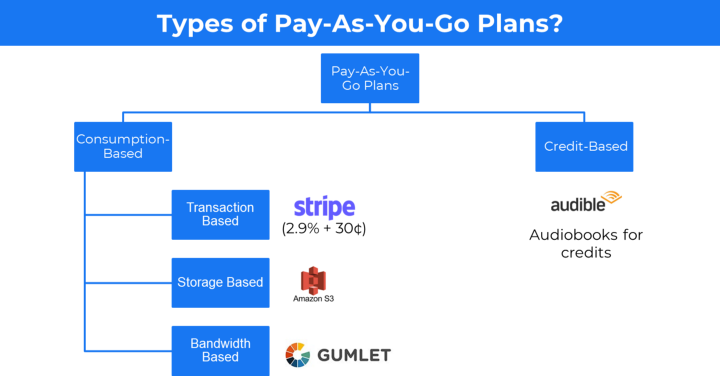
The pay-as-you business model is used when it is hard to bucket customers into a few pricing tiers.
Fee-for-service (FFS) business model 🔗
FFS’s business model is based on charging customers a fixed and variable fee for every successful payment.
Example: Stripe, Paypal and PayU
Stripe charges 2.9% + 30¢ per successfully executed payment transaction.
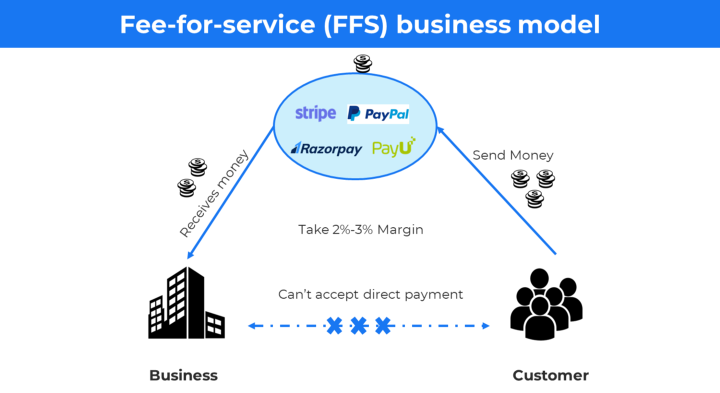
These companies provide a payment gateway to accept payment from the customer and then settle the money to a business account number.
EdTech business model 🔗
In the EdTech business model, you make money either by selling content or providing teaching as a service to the end user.
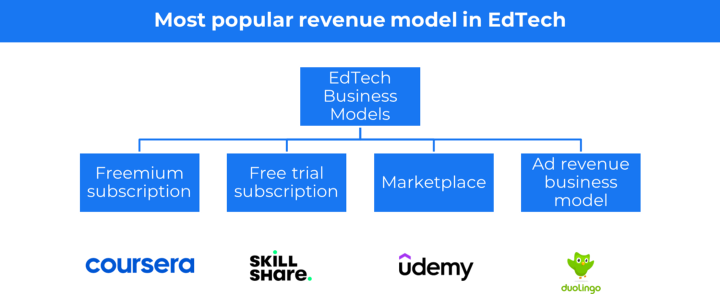
Types of Business Models in edtech
Freemium subscription — When course content is free but you need to pay for the course certificate e.g Coursera
Free trial subscription — When you offer a free trial followed by a monthly or annual subscription e.g SkillShare
Marketplace — Self-serving model where you choose what you want to learn from the open marketplace.
Ad revenue business model — The core product is free and the company generate money by showing ads to the massive user base they have.
Lock-in business model 🔗
‘Lock in’ aims to create a barrier for customers to switch from your brand or offering and instead move to a competitor offering.
It uses a combination of increasing switching costs or the effort to transfer (soft lock-in) or the superior brand experience or incentives
Example: Apple, SAP etc.
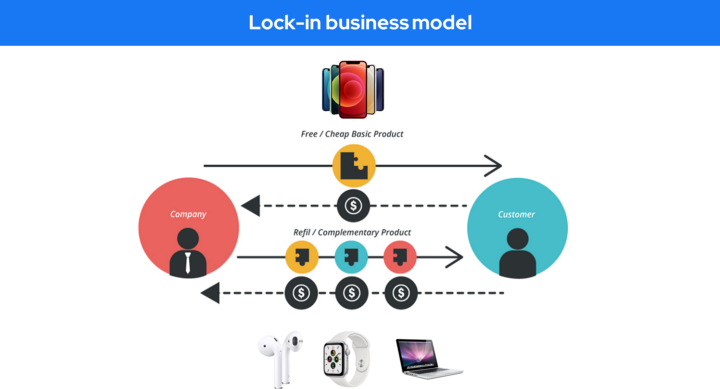
Apple sells you an iPhone and then lock you in with their ecosystem with other hardware (Watch, Airpod) and platform service like Apple Store, Apple Music, cloud, etc.
API licensing Business Model 🔗
An application programming interface, or simply an API, is a tool that allows third-party applications to communicate with your service.
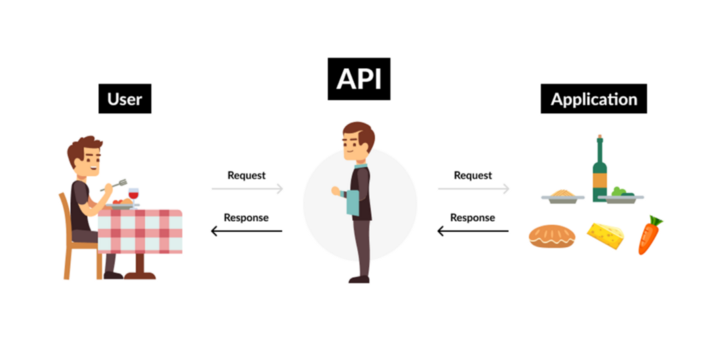
Uber and Airbnb use Google Maps APIs in their mobile app for easy navigation.
Example: Twilio (SMS), Sendgrid(Email), Google Map APIs(Map) etc.
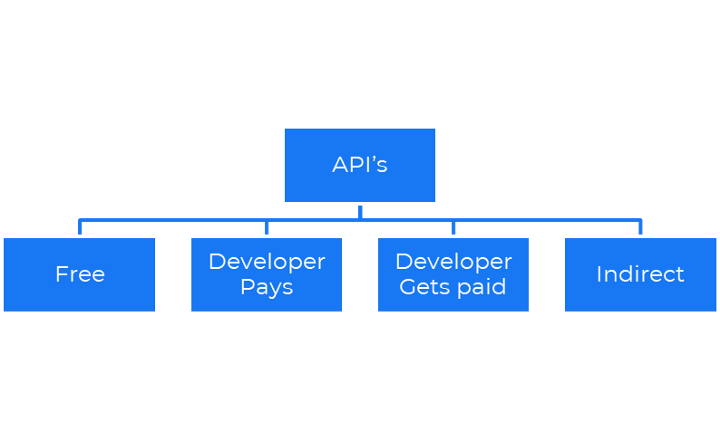
Here are the different types of APIs business model
- Free: Simplest API-driven business model which allows app developers to access APIs freely.
Example: Facebook, and Google Translate. - Developer Pays: This model operates in a form where application developers have to pay for the services provided
Example: AWS, Twilio, Github, Stripe etc. - The developer gets paid: These are the paid developers or content distributors who are distributing the APIs using their content.
Example: AdSense, Amazon affiliate etc.
Open-source business model 🔗
Open-source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance for personal use.
Example: Android, Java, Firefox etc.

In 2018 Google paid $435.702 million to Mozilla for Google as their default search engine.
Here are six ways how open-source software makes money.
- Paid support — The Project maintainer has a lot of knowledge about the codebase and he can charge for personalization.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) — Offer a complete database Solution for free but paid Monitoring tool. Example: MongoDB Atlas
- Open-core model — Better GUI alternative (R studio) for open-source projects.
- GitHub sponsors — 100% of sponsorships go to the developers.
- Paid feature requests — Get Paid To Build Open Source Extensions for Existing Products
Data as a business model 🔗
If the app or algorithm collects data from customers to improve the system or monetize it by adding value to other companies.
Example: Open AI GPT3 model becomes smarter as people use it.
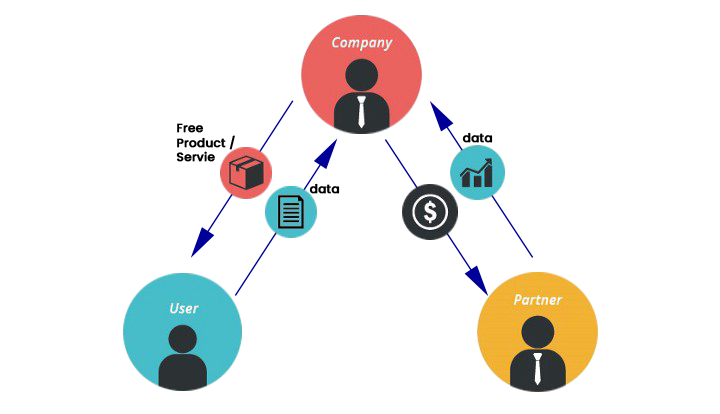
A popular free check-in app Foursquare allows users to share their locations on check-ins.
Later they compiled massive databases to help retail companies like Starbucks to find user clusters to open new stores.
Blockchain Business Model 🔗
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows other companies and business to deploy their smart contract without any central authority like AWS, Digital ocean etc
Example: Ethereum, Solana, Alchemy etc
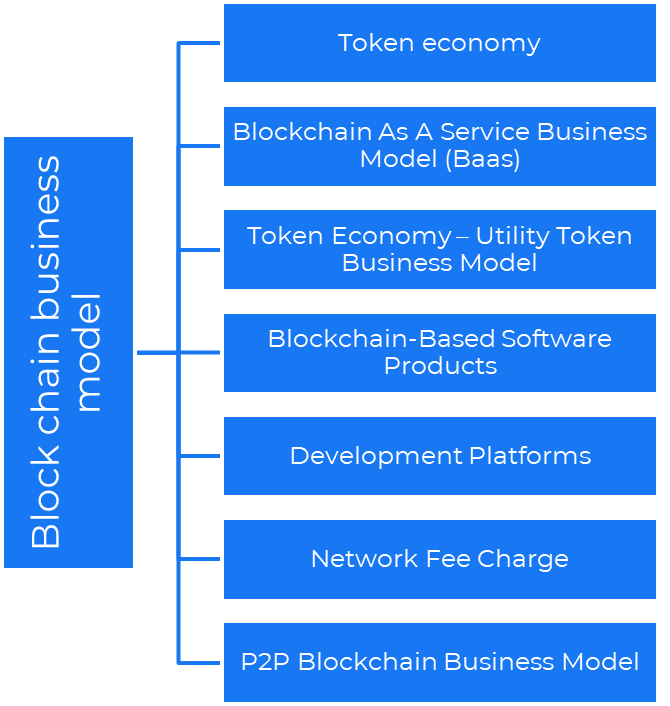
Types of Blockchain business Models
- Token Economy or Utility Token Business Model is when a company issue some token as one of the mechanisms to reward the token miner or token holder. Example: Solana and Ethereum
- P2P Blockchain Business Model — The peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain enables end-users to interact with each other directly. Example: IPFS
- Blockchain As A Service Business Model (BaaS) — BaaS is about providing ecosystem services like Microsoft (Azure) and Amazon (AWS) but in Web3 space. Example: Bitcoin and Ethereum i.e. Ethereum Blockchain as a Service (EBaaS).
- Blockchain-Based Aggregators — AWS for blockchain which means you will simply do an API call for your favorite blockchain, and you can use that service. Example: Alchemy is a node provider for a variety of blockchains.
Freeterprise business model 🔗
In the freeterprise (free & enterprise) business model the free professional accounts are driven into the funnel through the free product and later convert into a B2B/enterprise account.
Example; Slack and Zoom
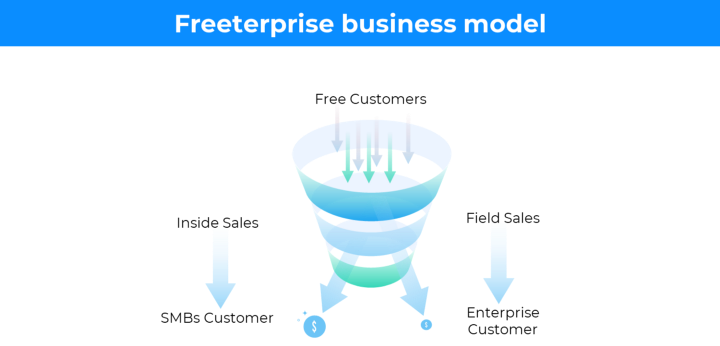
Some companies use collaboration as the growth engine in the Freeterprise model;
You can start from a single free professional account, and pull a whole organization into that, to transform it into an enterprise.
Razor blade business model 🔗
It is Widely used in hardware items where one item is sold at a low price or at losses and generates profits from refills or add-ons.
Examples: Gillet razor and blades; Coffee machine and coffee beans; HP Printer and Cartage; etc.
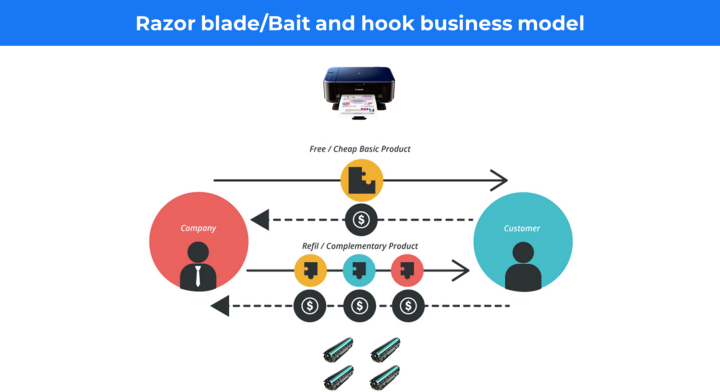
Benefits of the Razor-Razorblade Approach
- Reduces customer risk of trying the product
Allows customers to try the products and services without a substantial upfront cost. - The constant revenue stream from the product
Potentially resulting in sales many times over the initial outlays.
Direct-to-consumer (D2C) business model 🔗
In the D2C business model, the brand cut out the middleman and sells its product directly to the end consumer from its website using a third-party logistic partner.
Examples: GymShark, Kylie Cosmetics etc.
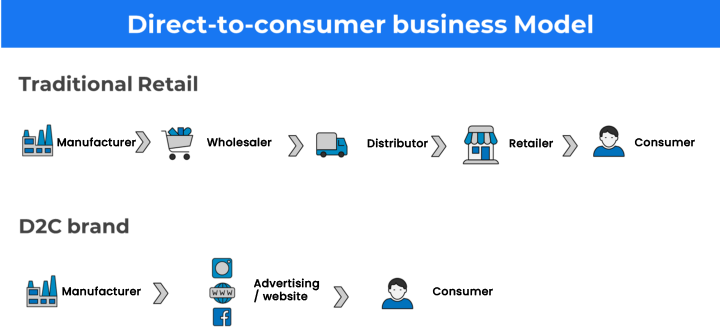
Brands using the D2C business model can only expand using online channels like Websites, Marketplaces(Amazon, eBay ) etc
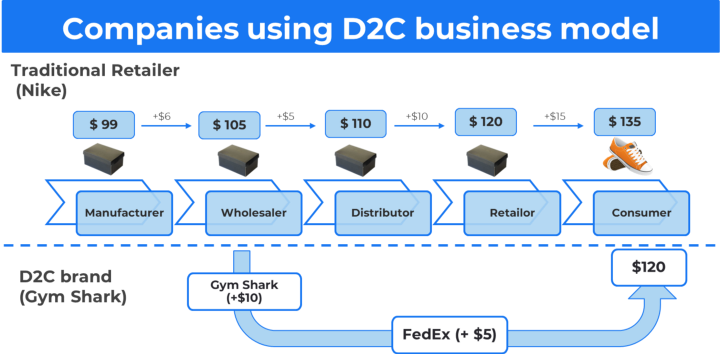
Benefits of using the D2C business model
- No middlemen = Higher control over profits
- Gaining access to more targeted customer data: Demographic, Geographic
- More room for product testing
- A higher degree of personalization in your product range-Inventory Less
Private Label vs White Label business model 🔗
A private label/White label product is manufactured by a contract or third-party manufacturer and sold under the brand name.
The majority of the electronics products on amazon are manufactured in china and are white labelled under some brand name.
Example: Supplement and electronic products on amazon.
Brands specify their product quantity with the design label and the rest is taken care of by the Contract manufacturer
Franchise business model 🔗
Here the franchisee(Store owner) is using the trademark, branding, and business model of a franchisor (company).
Examples: Dominos, KFC, etc.
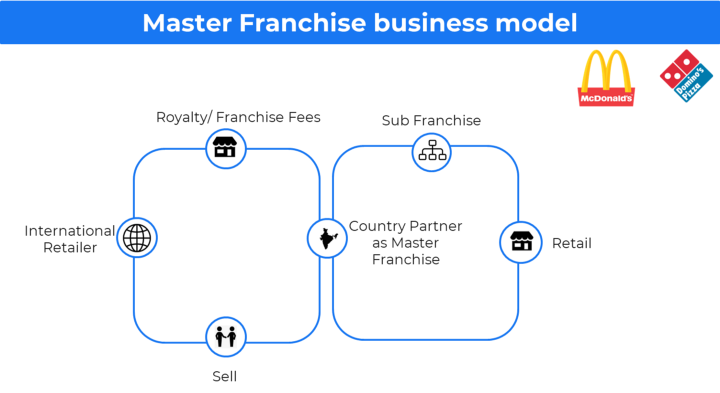
This business model is widely used by Quick service restaurants (QSR) like Subway, Domino, Burger King etc.
Comparing startup Franchise versus Restaurant:
| Franchise | Restaurant | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | initial franchisee fees | setup costs |
| Process | standardized procurement | process from scratch |
| Brand | well recognized brand | build your own brand |
| Business Model | established | test and trail |
| Failure | smaller chance | much larger |
Opening your restaurant increases the risk of failure hence many people choose to take a franchise.
Ad-based business model 🔗
Used by social media and search engine giants which use your search engine and interest data to show ads.
Examples: Google, Meta, TikTok and Snapchat
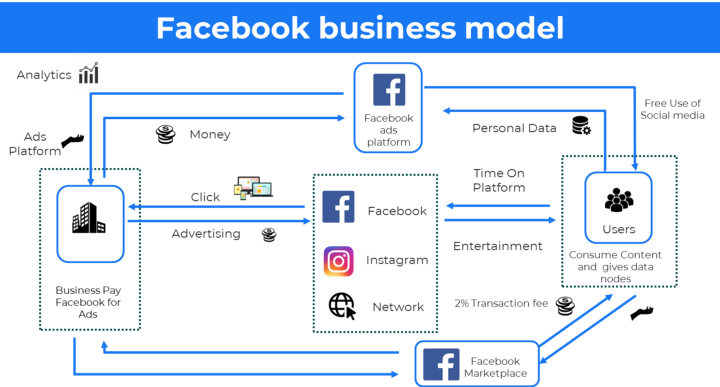
It keeps users out of the equation so they don’t pay for the service or product offered, e.g. Google users don’t pay for searches.
In return, they collected the data and then hyper-personalized these ads to make sure it generates maximum revenue for the business.
Octopus business model 🔗
It’s a diversification business strategy where each business unit like the tentacle of an octopus works independently but is connected to the main body.
Example: Oyo

OYO is the Airbnb for Asia which operates in everything from Hotel, Co-working, Co-living, Vacation homes etc
Transactional business model 🔗
The revenue is generated by directly selling an item or a service to a customer.
Widely used by e-commerce sites or any other product you purchase online.
Examples: GymShark, Goli

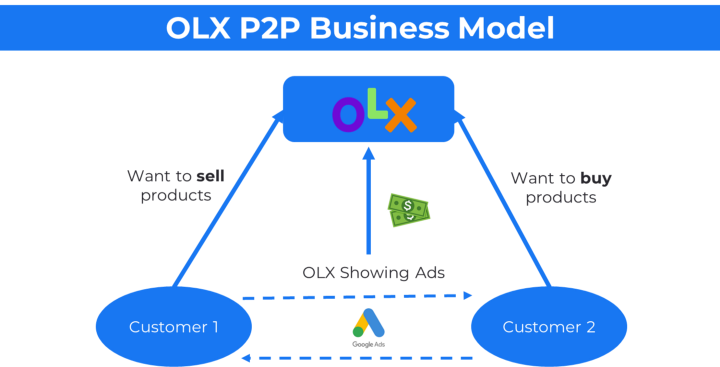
Peer-to-peer (P2P) Business Model 🔗
In a P2P business model, two individuals interact to buy and sell goods and services directly with each other without a third party or using a platform.
Example: OLX
P2P Lending as a business model 🔗
In the Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending business model one private individual (“P2P Lender”) lends/invests or borrows money from another private individual (“P2P Borrower”).
Example: Kabbage
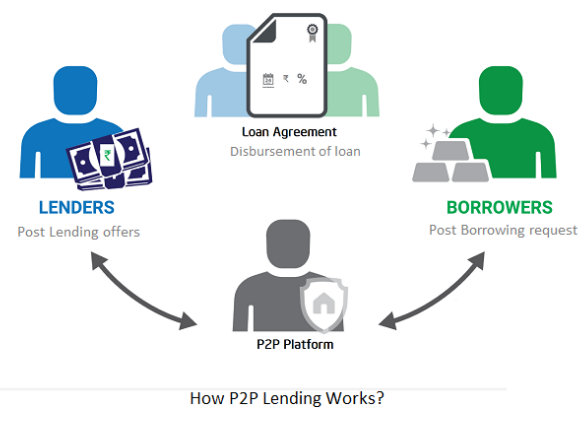
This is also known as“social lending” as it lets individuals lend and borrow money directly from each other without the use of an official financial institution as an intermediary.
Brokerage business model 🔗
Brokerage businesses usually charge a commission or fee to one or both parties in exchange for services rendered.
Examples: Robinhood, Coinbase and ebay
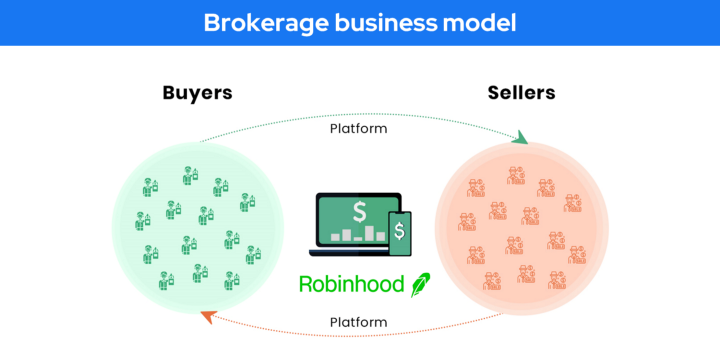
Brokerage businesses are common in the Real estate, Finance and Online Marketplace and usually operate on the following Model

- Buy/sell match model –They match buy and sell transactions and take a commission on that
Examples: Financial brokers, Insurance brokers etc - Classified-advertiser model — these brokers charge a fee to an advertiser based on the time, location, size, or nature of an advertisement. Example: Craiglist
Drop shipping Business model 🔗
Dropshipping is an e-commerce retail model that allows stores to sell products without keeping any physical inventory.
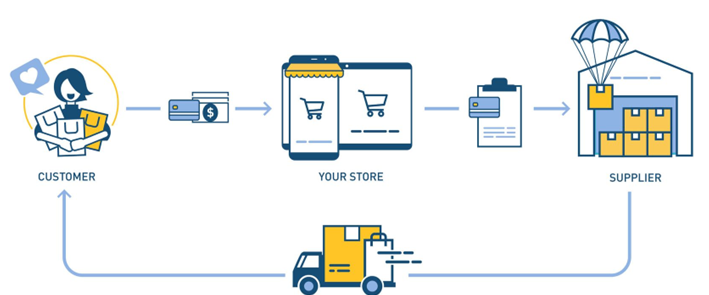
When a customer makes an order fulfil the order from a third-party supplier and logistic partners.
The Key Elements of the Dropshipping Business Model:
- Retailer — Product portfolio and customer experience
- The fulfiller — Managing, shipping, and fulfilling orders
- The customer — purchase the order
Advantages of drop shipping
- Less capital is required (Low overhead-No Inventory or warehousing)
- Easy to get started (Less than $100)
- Flexible working location
- Easier to test new product
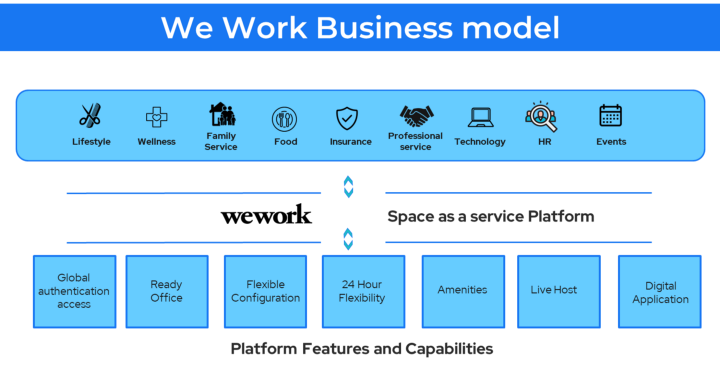
Space as a Service Business Model 🔗
It is based on the idea of a shared economy that provides millennials with the flexibility of living or working out of shared spaces without the headache of ownership or lease.
Example: WeWork, Airbnb
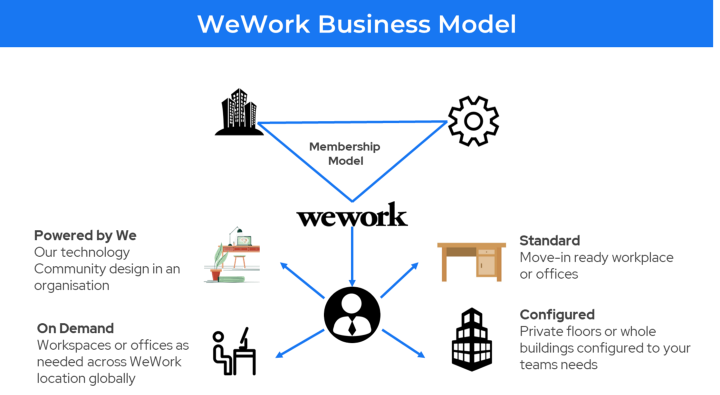
Companies like WeWork act as a middle layer between Real estate, legal compliances, maintenance and repair for business.
Third party logistic (3PL) business model 🔗
In the 3PL business model, the business outsources its products’ distribution, warehousing and fulfillment to an external logistics company which carries out these processes on its behalf.
Example: Fulfillment by Amazon, Ship Bob etc.

3PL partners handle both inbound and Outbound with warehousing, fulfillment and returns of certain goods for a fee.
Inbound logistics refers to purchasing and arranging the transportation of products from suppliers to your warehouse.
Outbound logistics refers to the flow of items through a company’s production line, warehouse and ultimately to the customer.

Last Mile delivery as a business model 🔗
Last-mile delivery consists of the set of activities in a supply chain that will bring the service and product to the final customer.
Examples: Gojek, Postmates, Rappi etc.
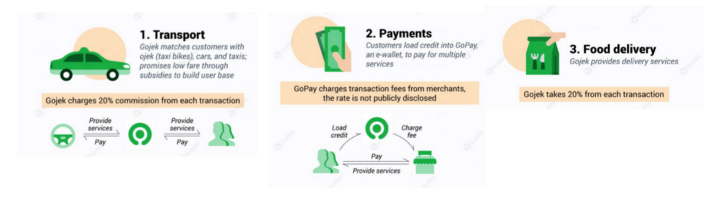
Last-mile is also intertwined with on-demand and usually has a peak cycle, especially in the evening.
Affiliate business model 🔗
Affiliate marketing is a revenue-earning strategy of promoting other companies’ products and charging commissions for every sale.
Examples: Amazon, Skillshare, Hubspot etc.

I am sure your favorite youtube is using these short amazon links to get 5% out of every sale that comes from these links.
Advantages of using the Affiliate business model:
- It enables many independent marketers to market on its behalf and earns a success fee or commission.
- Bring Transparency to the system as the influencers are provided with a unique tracking link and an online dashboard to see their earnings.
- Get access to promotional materials and learn about the latest deals.
The virtual goods business model 🔗
This is also known as the in-app purchase where you were required to make in-app purchases for an intangible product.
Examples: Candy Crush, Roblox, PubG etc

A consumable product is like purchasing currency in a game that’ll run out in due time.
A non-consumable product is one in which a user can purchase a permanent benefit without the need of buying it again and again.
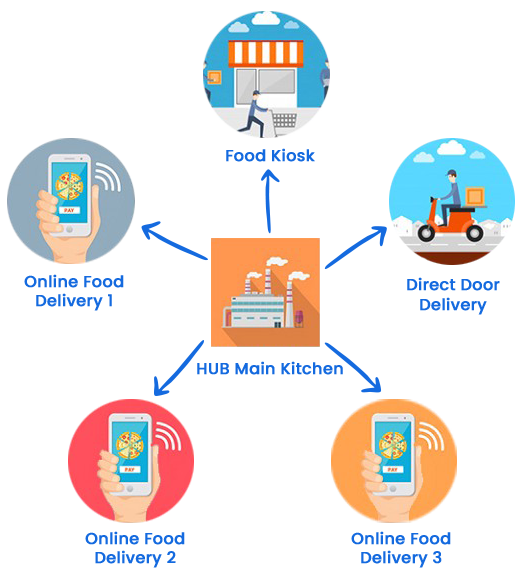
Cloud Kitchen Business Models 🔗
Also known as Ghost Kitchens, Dark Kitchens, Black Box Kitchens etc. A restaurant that sells meals exclusively through delivery channels. These restaurants offer no physical dine-in experience and instead cater only to customers eating meals at home.
Example: NextBite, Faaso’s
Crowdsourcing Business model 🔗
Crowdsourcing = Crowd acts as a source for a specific platform.
In a crowdsourcing business model, you voluntarily get help from people all over the world, without having to hire them as regular employees.
Types of Crowdsourcing Platforms
- Open-Source Software allows developers to access the software source code to modify or improve it.
Example: Linux operating systems and Firefox browsers. - Crowdfunding — Crowdfunding would be basically, with no expectations.
Example: The oculus headset.


